Immigration in India: Visa Types, Violations & New Legal Framework in 2025

Over the years, India’s immigration system has adapted to the changing global landscape, with digital advancements like the e-visa system and online FRRO services making visa processing and foreign national registrations more efficient. These updates have certainly improved the experience for travelers and expatriates, but the legal framework still somehow struggles to keep up with the growing concerns of visa violations, illegal immigration and the need for clearer enforcement protocols that both protect national interests and facilitate legitimate business operations.
Likely in response to such challenges, the government has recently tabled a new Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 in parliament, aiming to consolidate existing laws, strengthen security measures, and streamline policies for foreign nationals. This bill seeks to establish a more transparent and efficient system that balances international talent mobility with national security interests.
In this article, we aim to provide insights into India's evolving immigration landscape, particularly for expatriates and global mobility professionals. We'll explore its historical development, current regulatory framework, ongoing challenges, and recent reforms shaping cross-border mobility to India.
Evolution of Indian Immigration Landscape
Before India gained independence in 1947, immigration laws were primarily dictated by British colonial interests. However, after gaining independence, the Indian government has continuously evolved its immigration framework through amendments to existing legislation and introduction of new rules to adapt to changing economic landscapes and national priorities. The key legislative acts shaping immigration control can be traced through the following timeline:
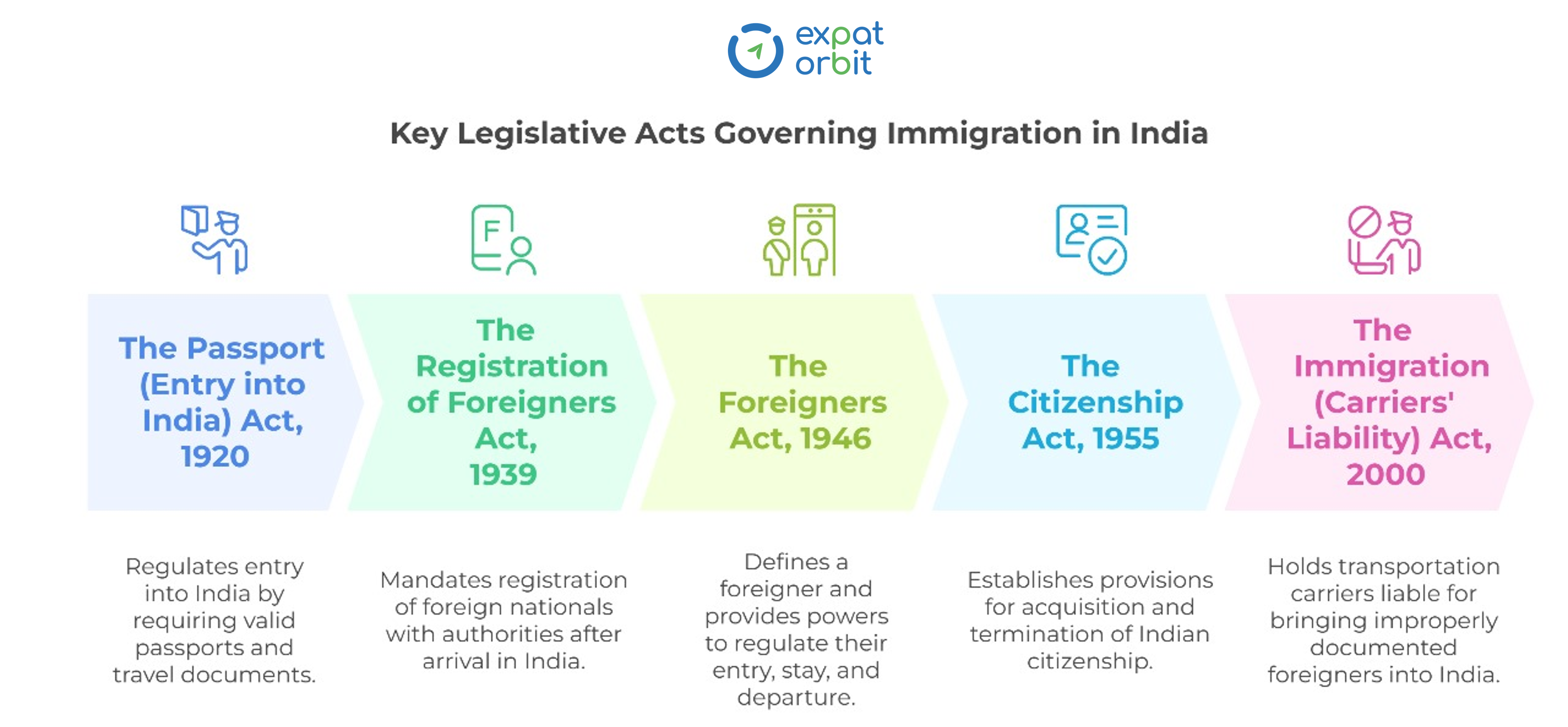
This timeline highlights the key legislative shifts that have shaped India's immigration policies. From the initial focus on basic border control to the comprehensive framework for managing citizenship and foreign nationals, each act reflects the evolving needs and priorities of the nation.
Existing Immigration Landscape
India offers distinct visa categories tailored to different professional needs, whether for employment, business expansion, or specialised projects. Below is a summary of different visa categories offered in India:

Selecting the right visa category is crucial for foreign nationals entering India, as it ensures compliance with immigration regulations and prevents potential legal complications during their stay. The appropriate visa not only facilitates a smooth assignment cycle but also determines the scope of employer obligations and expat’s permitted activities while in the country.
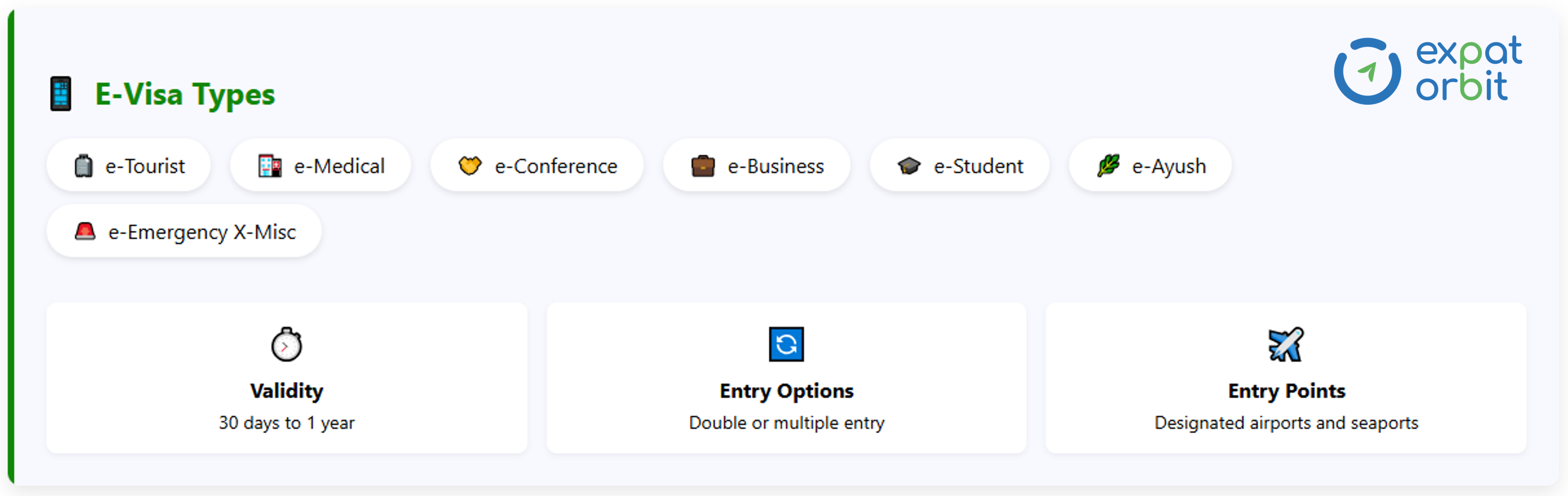
E-Visa
India also offers electronic visas through a streamlined online application process for short-term visitors. This system provides faster approvals and digital travel documentation, making entry more convenient for eligible travelers.
Click here to read more about different types of work visas in India.
After entering India, most long-term visitors must register with the Foreigners Regional Registration Office (FRRO), which oversees foreign nationals' stay in the country. Registration requirements vary by visa type, with Employment and Project visa holders typically required to register within 14 days of their arrival if the visa exceeds 180 days, while Business visa holders' obligations depend on their stay duration and specific visa endorsements. This mandatory process establishes legal residency status and enables proper monitoring of foreign nationals during their stay in India.
Learn more about FRRO registration for foreigners in India.
Visa Violations: Common Pitfalls and Growing Concerns
Visa compliance in India has become an increasingly scrutinised area of immigration enforcement, with authorities demonstrating heightened vigilance in recent years. Many organisations inadvertently fall into non-compliance through misconceptions about visa categories, such as using Business Visas for activities that legally require Employment Visas, or overlooking mandatory FRRO registrations for long-term stays.
Recent enforcement actions against both individuals and multinational corporations demonstrate the serious consequences of non-compliance, including financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Below are some common visa violations that have recently drawn regulatory attention, highlighting the risks for all stakeholder’s involved.

Sources: https://bit.ly/41Q2gQu, https://bit.ly/3DhsWAr, https://bit.ly/41CUojV, https://bit.ly/3XDJrgR
Above are some cases that represent common visa compliance challenges frequently encountered in India. In addition to these, common areas of non-compliance include failure to register with the FRRO, use of forged documents, working for multiple employers, and travelling outside India during pending visa extension applications.
For a deeper understanding of best practices and common pitfalls to avoid when hiring expatriates in India, refer to our article on Navigating Work Visas in India.
The Proposed Immigration Bill: A Step Toward Comprehensive Reform
India's immigration framework is based on decades-old policies rooted from an older geopolitical era. While these regulations provide a foundation for controlling foreign entry and stay, they lack clarity in some areas—such as institutional responsibilities for hosting foreign nationals, inter-agency coordination, and penalty frameworks for non-compliance.
Recognising the need for stronger and more structured immigration policies, the Indian government has introduced a new Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 to replace outdated regulations. Though yet to be passed, this bill likely aims to modernise India's immigration framework with several key changes including:
- Stricter penalties for visa violations
- Simplified laws for better clarity
- Clearer institutional responsibilities
- Tighter passport and visa rules
- Expanded authority for immigration officers
Conclusion
Understanding India's immigration framework remains fundamental for successful expatriate assignment in the country, as this complex system has transformed from its colonial-era foundations into today's nuanced visa categories. This evolution has created distinct compliance obligations that organisations must manage diligently. Proper visa classification, timely registration procedures, and meeting regulatory compliances form the cornerstone of effective expatriate management, helping companies avoid costly pitfalls.
Looking forward, India's proposed Immigration and Foreigners Bill signals further refinement of this framework. By potentially strengthening enforcement mechanisms while streamlining legitimate business travel, these changes reflect India's continuing effort to modernise its approach to global mobility management and international business engagement.
At Expat Orbit, we support global companies and expatriates in ensuring a compliant immigration journey to India, from selecting and applying for the appropriate visa category to managing ongoing registrations and compliance requirements. For any queries or assistance with your global mobility needs, email at [email protected] or schedule a call with our experts.
